GIS Workflow Insights for Renewable Energy Projects

GIS is changing how renewable energy projects are planned and managed. It combines mapping with data analysis to help teams make better decisions, save time, and reduce costs. Here’s a quick summary of how GIS supports renewable projects:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Track site conditions and project progress instantly.
- Data Integration: Merge topography, environmental data, and land records into one platform.
- Field Collaboration: Use mobile tools to update and share data on the go.
- Decision Support: Visualize risks, resources, and layouts for smarter planning.
Key Benefits:
- Find the best locations for projects by analyzing factors like wind/solar potential, land ownership, and environmental impact.
- Simplify the approval process with detailed reports and visual tools.
- Manage construction and operations efficiently with real-time tracking and performance monitoring.
GIS helps renewable energy teams avoid delays and cost overruns, which affect 90% of global infrastructure projects. Tools like Matidor make it easier to centralize data, improve communication, and keep projects on track.
Real Time Renewable Energy Workflows with ArcGIS Velocity
GIS Workflow Steps for Renewables
GIS plays a key role in renewable energy projects, guiding every step from data collection to decision-making. Here’s how teams use GIS to streamline their workflows.
Getting and Combining Data
The first step is gathering and merging various datasets like topography, wind patterns, and land ownership. A centralized platform makes this process smoother by letting field teams input real-time data while office staff layer it with existing information.
| Data Type | Purpose | Collection Method |
| Topographical | Assess site suitability | Satellite imagery, ground surveys |
| Environmental | Evaluate project impact | Field measurements, public databases |
| Land Records | Define property boundaries | County records, legal documents |
| Resource Data | Analyze energy potential | Weather stations, historical records |
Making Sense of Data
GIS tools transform raw data into actionable insights. Visual maps and spatial analysis help teams spot patterns, assess risks, and design efficient layouts.
During this stage, GIS is used to evaluate terrain for equipment placement, identify environmental constraints, calculate energy output, and plan infrastructure. These insights ensure teams can track progress and create detailed reports.
Team Updates and Reports
Once analysis is complete, teams need to share findings quickly and clearly. Platforms enable real-time updates, keeping everyone in sync and informed.
Real-time updates help teams spot issues early and act fast, ensuring projects stay on track and run efficiently. This ongoing communication is key to maintaining momentum and alignment across all stakeholders.
GIS Use in Project Stages
GIS plays a key role in renewable energy projects, guiding them from the planning phase all the way through to operation.
Finding the Right Location
Choosing the right site for renewable energy projects involves analyzing a variety of factors. GIS tools make this process easier by allowing teams to layer and examine multiple data sets at once:
| Assessment Factor | GIS Application | Impact on Decision |
| Resource Potential | Wind/solar data mapping | Pinpoints areas with high energy output potential |
| Land Constraints | Ownership/zoning analysis | Helps avoid legal or regulatory issues |
| Environmental Impact | Habitat/watershed mapping | Ensures compliance with environmental regulations |
| Grid Connection | Infrastructure proximity | Reduces connection costs and logistical challenges |
These mapping tools help teams identify the best locations by balancing energy potential with real-world constraints, making it easier to secure approvals and move forward.
Getting Approvals
The permitting process can make or break a project’s timeline. GIS simplifies this step by offering detailed documentation and visual tools that help communicate with stakeholders. Teams can:
- Create environmental impact reports
- Develop visual simulations for public and community feedback
- Track permits across different jurisdictions
- Maintain records of compliance with local regulations
With clear and organized data, the approval process becomes faster and smoother, setting the stage for successful project execution.
Building and Running Projects
Once construction begins, GIS plays a critical role in managing projects efficiently. Its real-time tracking features allow teams to stay on top of progress and address issues as they arise.
Construction teams rely on GIS to:
- Monitor equipment and resource deployment
- Track construction progress
- Document compliance with regulations
- Coordinate activities among contractors
For operational facilities, GIS supports:
- Tracking performance metrics
- Scheduling maintenance
- Conducting environmental assessments
- Optimizing resource usage
It’s worth noting that 90% of global infrastructure projects experience delays or go over budget [1]. By using GIS, teams can access real-time data and foster better collaboration, helping to avoid these common pitfalls and keep projects on track. Modern GIS platforms are critical tools for ensuring projects are completed efficiently and within budget.
Problems and Solutions in GIS
Main GIS Hurdles
Renewable energy projects often encounter GIS-related challenges that can disrupt timelines and inflate budgets. Key problem areas include data management, collaboration, field operations, and system integration.
| Challenge | Impact | Common Issues |
| Data Management | Project delays | Incomplete datasets, outdated information |
| Team Collaboration | Communication gaps | Fragmented data access, inconsistent updates |
| Field Operations | Cost overruns | Lack of real-time visibility, inefficient resource allocation |
| System Integration | Workflow issues | Incompatible tools, complex setup |
Addressing these issues is crucial for smoother GIS workflows in renewable projects. Below are practical tips to improve GIS usage.
Tips for Better GIS Use
- Streamline Data Collection
Use dependable tools that allow field teams to update data on the go. Mobile-friendly solutions ensure timely and accurate information reaches project stakeholders. - Improve Team Collaboration
Centralize your data on a single platform with real-time updates and easy export options. This ensures everyone works with the same, up-to-date information.
“Streamline collaboration and decision-making on one single platform that allows owners, consultants, and contractors to access and share the same data in real time. Say goodbye to disjointed communication and fragmented data management, which lead to project delays, costly errors, and misaligned expectations.” – Matidor.com [1] - Use Real-time Tracking
Map-based tracking tools help teams spot potential problems early. This proactive approach can prevent small issues from turning into major setbacks. - Invest in User Training
Proper training ensures users can fully utilize GIS tools, leading to more efficient workflows and better project outcomes.
Matidor GIS Tools for Renewables
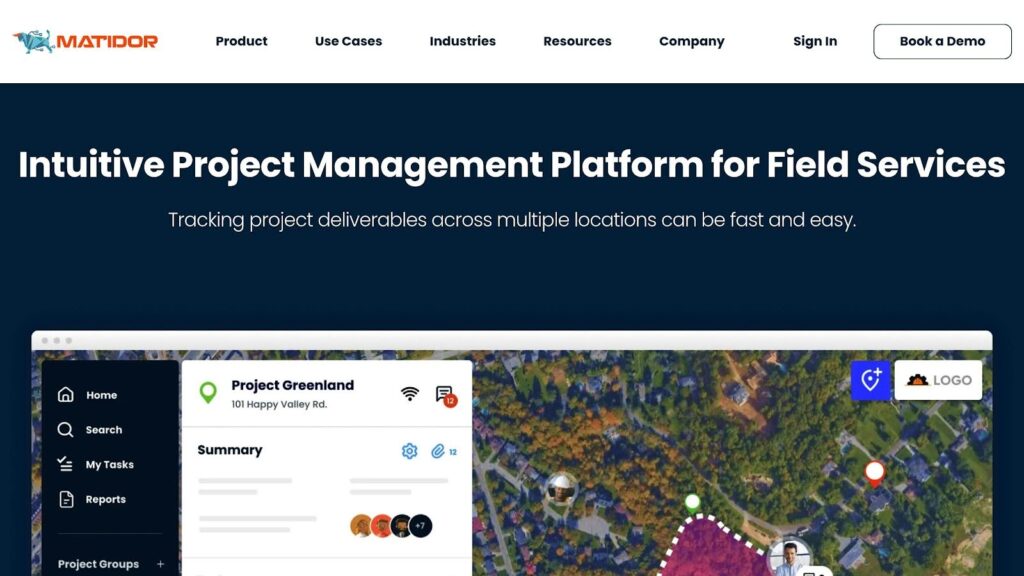
Matidor enhances GIS workflows for renewable energy projects with a specialized set of tools. Its map-based interface acts as a central hub, giving teams real-time access to project data specifically designed for renewable energy initiatives.
Matidor’s Main Tools
| Tool Category | Key Features | Advantages |
| Field Operations | Mobile app integration, offline mode | Collect and update data from anywhere |
| Data Management | GIS visualization, centralized storage | Keep all project information in one place |
| Collaboration | Multi-user access, role-based permissions | Simplify communication among stakeholders |
| Reporting | Custom templates, data export options | Easily create project updates and summaries |
These tools help improve project workflows and make team collaboration more effective.
What Matidor Delivers
Matidor’s GIS tools bring meaningful improvements to renewable energy projects by streamlining processes and boosting team productivity.
“Very pleased overall – provides us with the project tracking capabilities required internally and for consultants.” – April, Sustainability Analyst [1]
Here’s what Matidor brings to the table:
- Real-time Visibility: Use the map-based interface to monitor budgets and track task progress instantly.
- Data Integration Made Simple: Combine tasks, budgets, GIS data, forms, and files into one easy-to-access platform.
- Improved Stakeholder Communication: Ensure project owners, consultants, and contractors are always working with the same up-to-date information.
- Customizable Reporting: Generate reports tailored to your needs or use ready-made templates for quick updates.
Summary
GIS workflows are transforming how renewable energy projects are planned, executed, and monitored. With 90% of global infrastructure projects experiencing delays or cost overruns [1], GIS solutions help keep projects on schedule and within budget. Here are three key ways GIS makes a difference:
Real-Time Project Insights
Modern GIS tools offer instant access to project information through interactive maps. Teams can quickly spot potential problems and make informed decisions. This visual approach ensures stakeholders stay up-to-date on progress and resource use.
Improved Field Operations
Field teams equipped with mobile GIS tools can collect and update data on the go. This reduces delays caused by manual data entry and boosts operational efficiency.
Better Team Collaboration
GIS platforms bring all project data together in one place. Teams can analyze spatial data alongside project metrics, enabling quicker, smarter decisions. This approach aligns teams and helps projects hit milestones faster.
Using GIS effectively reduces risks and enhances outcomes for renewable energy projects. Centralized GIS data supports smoother project management and helps drive future success in the renewable energy sector.”I would recommend Matidor to any field service or EHS consulting company to ultimately lower liabilities and streamline critical project management workflows.” – Nathan, Managing Partner [1]